5.3 Additional Questions :
Answer the following questions :
1. Name and explain in brief the four major domains of the earth.
Ans: The four major domains of the earth are (i) Lithosphere (ii) Atmosphere (iii) Hydrosphere (iv) Biosphere .
The solid portion of the earth on which we live is called the Lithosphere. The gaseous layers that surround the earth, is the Atmosphere, where oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and other gases are found. Water covers a very big area of the earth’s surface and this area is called the Hydrosphere. The hydrosphere comprises water in all its forms, that is, ice, water and water vapour. The Biosphere is the narrow zone where we find land, water and air together, which contains all forms of life.
2. What are the two main division of the earth’s surface.
Ans: The two main divisions of the earth’s surface are the large landmasses are known as the continents and the huge water bodies are called the ocean basins.
3. Write a few sentences on the following continents.
Ans :
i) Asia – Asia is the largest continent. It covers about one – third of the total land area of the earth. This continent lies in the north eastern hemisphere. The Tropic of Cancer passes through this continent.
ii) Europe – Europe is much smaller than Asia. This continent lies to the west of Asia. The Arctic Circle passes through it.
iii) Africa – Africa is the second largest continent after Asia. The equator or 00 latitude runs almost through the middle of this continent.
iv) North America – North America is the third largest continent of the world. It is linked to South America by a narrow strip of land called the Isthmus of Panama.
v) South America – South America lies mostly in the Southern Hemisphere. South America has the world’s largest river, the Amazon.
vi) Australia – Australia is the smallest continent that lies entirely in the Southern Hemisphere. It is surrounded on all sides by the oceans and seas. It is called an Island continent.
vii) Antarctica – Antarctica, completely in the Southern Hemisphere, is a huge continent. The south pole lies almost at the centre of this continent.
4. There is a need to limit the use of the resources. Why .
Ans: Emission from industries, thermal power plants and vehicles, pollutes the air. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an important constituent of air. But increase in the amount of CO2 leads to increase in global temperatures. This is termed as global warming.
There is thus, a need to limit the use of resources of the earth to maintain the balance of nature between the domains of the lithosphere, the atmosphere and the hydrosphere.
a) Draw a neat picture of the biosphere.
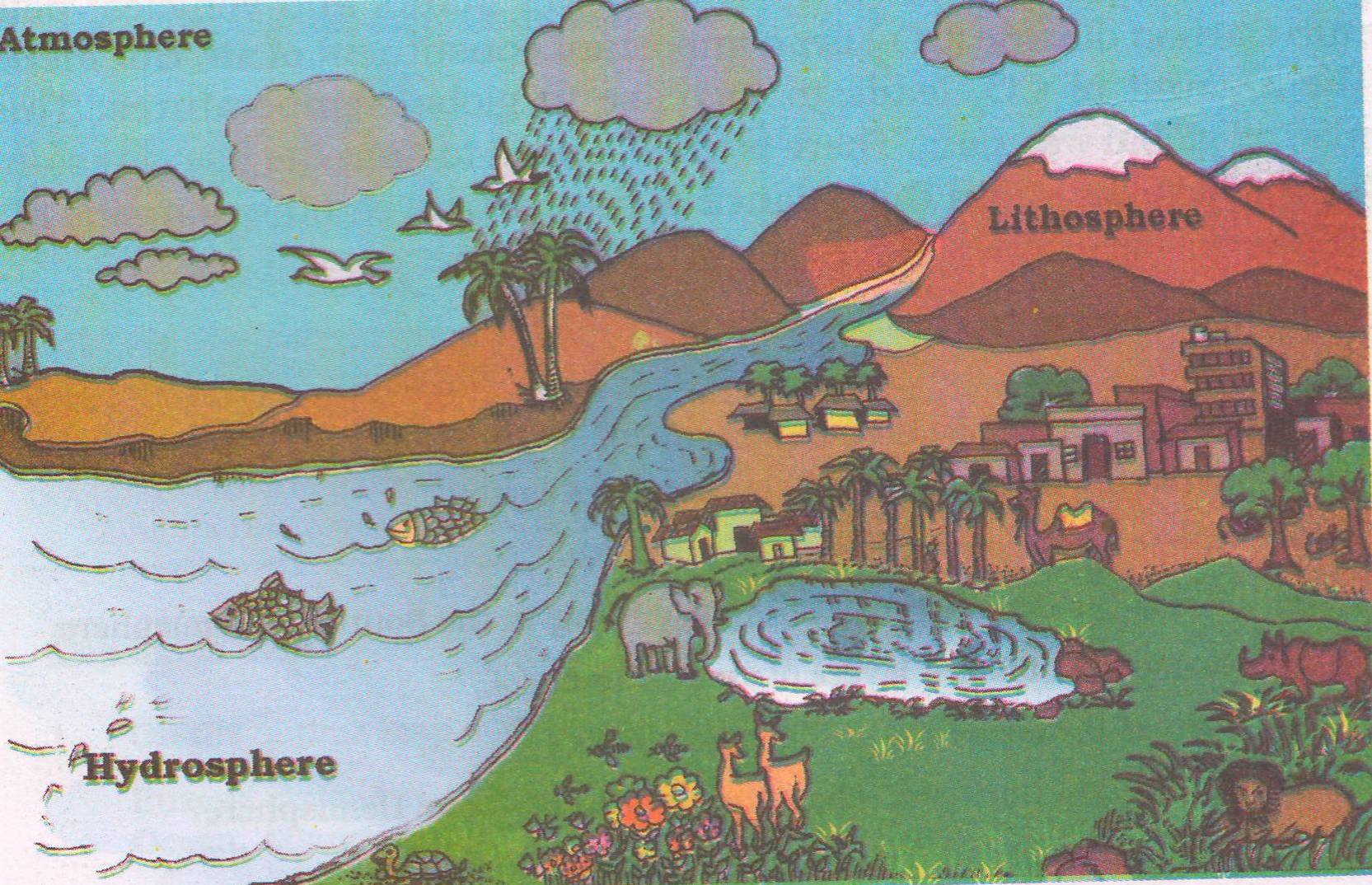
Define the following:
1. Lithosphere :- The solid portion of the earth on which we live is called as the Lithosphere.
2. Atmosphere :- The gaseous layers that surround the earth , is called as the Atmosphere.
3. Hydrosphere:- A hydrosphere is the total amount of water on the earth .
4. Biosphere :- The biosphere is the narrow zone where we find land, water and air together , here all forms of life can live.
5. Continents:- The large landmasses are known as the continents.
6. Ocean basins:- The huge water bodies are called ocean basins.
7. Global warming:- Increase in the amount of carbon dioxide leads to increase in global temperatures. This is termed as global warming.
8. Plant kingdom:- Plant kingdom includes all the plants on the earth.
9. Animals kingdom:- Animal kingdom includes all the animals on the earth.
10. Wind:- Moving air from high pressure to low pressure is known as wind.
Give reasons :
1. Why is the atmosphere an important aspect of earth.
Ans: The atmosphere is an important aspect of earth because it provides us with the air to breathe and protects us from the harmful effects of the sun’s rays.
2. Carbon dioxide helps in keeping the planet warm. Give reason.
Ans: Carbon dioxide absorbs the heat radiated by the earth this helps in keeping the planet warm.
3. Why do climbers experience problem in breathing.
Ans: The climbers experience problem in breathing due to decrease in the density of air.

