Q1) You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below.
1. Carbohydrates 2. Proteins 3. Fats 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6. Roughage
Different ways of taking food:
1) What is the type of food and mood of feeding of the following animals? Write down your observations in the given table. You may find the list of modes of feeding given below the table helpful.
| Name of animals | Kind of food | Mode of feeding |
| Snail | Insects, lower plants | Scraping |
| Ant | food particles | Scraping |
| Eagle | Small birds, small animals | Capturing and eating |
| Humming Bird | nectar of flowers | Sucking |
| Lice | blood | Sucking |
| Butterfly | nectar of flowers | Sucking |
| Housefly | Animals and human waste | Sucking |
DIGESTION IN HUMANS :
i) Wash your hands. Look into the mirror and count your teeth.
1. How many kinds of teeth could you find?
Ans: Four
2. Take a piece of apple and eat it. Which teeth do you use for biting and cutting?
Ans: Incisors
3. Which one for piercing and tearing?
Ans: Canines
4. Which ones are used for chewing and grinding?
Ans: Premolars and Molars
| Type of Teeth | Number of teeth | Total | |
| Lower jaw | Upper jaw | ||
| Cutting and biting teeth | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| Piercing and tearing teeth | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| Chewing and grinding teeth | 10 | 10 | 20 |
1. Why is there a change in colour in the test tubes?
Ans:
Test tube A: blue black colour appeared because of presence of starch.
Test tube B: colour remains unchanged due to digestion of starch into sugars by the action of saliva.
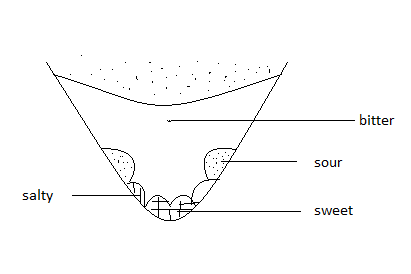
2. Which areas of the tongue can detect sweet, salty, sour and bitter substances?
Write down your observations and label fig 2.6.
Ans :
3. Paheli wants to know how food moves in the opposite direction during vomiting.
Ans: An intense pressure is formed in the stomach when the food is not accepted by the stomach. As a result the contents of the stomach is pushed back in form of vomiting.
Digestion in grass – Eating animals :
Q1. Paheli wants to know why ruminant animals cannot chew food properly at the time they take it in.?
Ans: Ruminant animals like cow feed mainly on grass that contains cellulose which is difficult to digest. At the time they take in food, it is moistened and sent for cellulose digestion in rumen and they get more time to eat.
Q2. Boojho wants to know why we cannot digest cellulose like the cattle do.
Ans: We cannot digest cellulose because we do not have the bacteria that is needed for digestion of cellulose as in the case of cattle like cow.
TEXTUAL EXERCISES :
1. Fill in the blanks:
a) The main steps of digestion in humans are ____________ and ___________ .
b) The largest gland in the human body is _________ .
c) The stomach releases hydrochloric acid and _________ juices which act on food.
d) The inner wall of the small intestine has many finger like outgrowth called _________ .
e) Amoeba digests its food in the __________ .
Ans:
a) ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and digestion b) liver
c) digestion d) villi e) food vacuole.
2. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
a) Digestion of starch starts in the stomach. (T/F)
b) The tongue helps in mixing food with saliva. (T/F)
c) The gall bladder temporarily stores bile. (T/F)
d) The ruminants bring back swallowed grass into their mouth and chew it for some time. (T/F)
Ans:
a) F b) T c) T d) T .
3. Tick (√) mark the correct answer in each of the following:
a) Fat is completely digested in the ___________ .
i) stomach ii) mouth iii) small intestine iv) large intestine
b) Water from the undigested food is absorbed mainly in the _____________ .
i) stomach ii) food pipe iii) small intestine iv) large intestine
Ans:
a) iii b) iv
4. Match the items of column I with those given in column II :
Column I Column II
i) Carbohydrates a) Fatty acids and glycerol
ii) Proteins b) Sugar
iii) Fats c) Amino acids
Ans:
i) b ii) c iii) a
5. What are villi? What is their location and functions?
Ans: The inner walls of the small intestine have thousands of finger like outgrowths. These are called villi. Villi are located inside the small intestine and increases the surface area for absorption of the digested food.
6. Where is the bile produced? Which component of the food does it digest?
Ans: Bile is produced by the liver and stored in the gall bladder. It helps in digesting fats.
7. Name the type of carbohydrates that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Give the reason also.
Ans: Cellulose is the type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. It is because a certain bacteria that can digest cellulose is present in ruminants but absent in humans.
8. Why do we get instant energy from glucose?
Ans: Glucose is the simplest form of carbohydrate which can be easily absorbed by the body to give energy.
9. Which part of the digestive canal is involved in :
i) absorption of food _________ .
ii) chewing of food __________ .
iii) killing of bacteria _________ .
iv) complete digestion of food ________ .
v) formation of faeces _________ .
Ans:
i) small intestine ii) buccal cavity iii) stomach
iv) small intestine v) large intestine
10. Write one similarity and one difference between the nutrition in amoeba and human beings.
Ans: Similarity: Digestive juices are secreted by humans as well as amoeba to digest food. Difference: In humans, food is taken in via mouth (buccal cavity). whereas in amoeba, food is taken in via pseudopodia.
11. Match the items of Column I with suitable items in Column II :
Column I Column II
a) salivary gland i) Bile juice
b) stomach ii) Storage of undigested food
c) liver iii) Saliva secretion
d) rectum iv) Acid release
e) small intestine v) Digestion is complete
f) Large intestine vi) Absorption of water
Ans:
a) iii) b) iv) c) i) d) ii) e) v) f) vi) .
12. Label fig 2.11 of the digested system (refer human digestive system) .
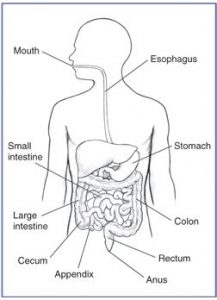
13. Can we survive only on raw leaf vegetables / grass? Discuss .
Ans: No, raw leafy vegetables / grass mainly consists of cellulose which cannot be digested by us due to the lack of certain bacteria. So also our body needs a complete balance of different nutrients.
Extended learning – Activities :
Q1. Visit a doctor and find out:
i) Under what conditions does a patient need to be on drip of glucose?
Ans: A patient needs to be on a drip of glucose when he/she is unwell, unable to eat, body is weak and needs energy.
ii) Till when does a patient need to be given glucose?
Ans: Till the patient is well.
iii) How does glucose help the patient recover?
Ans: Glucose is a simple sugar which is easily absorbed in the blood and hence it provides instant energy.
Q2. Find out what vitamins are and get the following information.
i) Why are vitamins necessary in the diet?
Ans:
i) Vitamins are essential nutrients that help our body to stay healthy and function properly
ii) Vitamins are needed for :
a) proper functioning of our body.
b) to fight off diseases .
ii) Which fruits or vegetables should be eaten regularly to get vitamins .
Ans: Green leafy vegetables, all fruits provide vitamins.

