Answer the following questions :
1. You read that one of the main functions of the judiciary is ‘Upholding the law and enforcing Fundamental Rights’. Why do you think an independent judiciary is necessary to carry out this important function?
Ans: The judiciary in our country performs several important functions:
i) Firstly, it upholds the law of the land .
ii) It enforces the Fundamental Rights of the citizens of the country.
The functions of the judiciary can only be carried out if it is independent free from the influence of the Executive and members of the legislative Houses whether at state level or central level. Judges should be appointed according to procedures laid down and their qualification as decided by the Constitution. Their tenure should be fixed.
2. Re –read the list of Fundamental Rights provided in Chapter-1. How do you think the Right to Constitutional Remedies connects to the idea of judicial review?
Ans: This allows citizens to move the court if they believe that any of their Fundamental Rights have been violated by the state.
As far as power of judicial review is concerned it has the right to strike down particular laws passed by the parliament, if it believes that these violation of the basic structure of the constitution. It can intervene and direct the Executive that is the Government.
3. In the Following illustration, fill in each tier with the judgments’ given by the various courts in the Sudha Goel case. Check your responses with others in class.
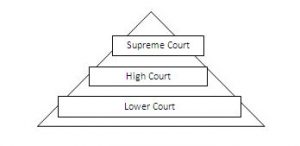
Ans: The judgements given by the various courts are as follows:
i) The Lower Court convicted Laxman, his mother and his brother and sentenced all three of them to death.
ii) The High Court, after hearing the arguments of all the lawyers, decided that Sudha had died due to an accidental fire caused by kerosene stove. Laxman, Shankutala and Subhash Chandra were acquitted.
iii) The Supreme Court heard the arguments of the lawyers and reached decision that was different from that of High Court. They found laxman and his mother guilty but acquitted brother -in- law Subhash Chandra because they did not have enough evidence against him. The Supreme Court decided to send the accused to prison for life.
4. Keeping the Sudha Goel case in mind, tick the sentences that are true and correct the ones that are false:
1. The accused took the case to the High Court because they were unhappy with the decision of the Trial Court.
2. They went to the High Court after the Supreme Court had given its decision.
3. If they do not like the Supreme Court verdict, the accused can go back again to the trial court.
Ans:
1. True
2. False. Because the decision of the Supreme Court is final and binding.
3. False. Because the Supreme Court is the apex court of the country and no appeal can be filed against the decision of the Supreme Court.
5. Why do you think the introduction of Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in the 1980’s is a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all?
Ans: In the 1980’s a significant step in ensuring access to justice for all because it allowed an individual or organization to justice to file PIL in High Court or the Supreme Court on behalf of those whose rights have been violated.
The legal process was greatly simplified d even a letter or telegram addressed to the Supreme Court or High Court could be treated as PIL.
6. Re-read excerpts from the judgments on the Olga Tellis vs Bombay Municipal Corporation case. Now write in your own words what the judges meant when they said that the Right to Livelihood was part of the Right to Life.
Ans: The following excerpts from the judgment point are out the ways in which judges linked the issue of the Right to Life to that of Livelihood are:
i) The sweep of the Right to life conferred by Article 21 is wide and far reaching. Life means something more than mere animal existence. It does not mean that life cannot be extinguished or taken away. For example, by the imposition and execution of the death sentence, except according to procure established by law.
ii) The eviction of a person from a pavement or slum will inevitably lead to the deprivation of his means of livelihood is a proposition which does not have to be established in each individual case. In the present case that facts constituting empirical evidence justify the conclusion that the petitioners live in slums and on pavements because they have small jobs to nurse in the city and for them there is no other place to live.
7. Write a story around the theme, ‘Justice delayed is justice denied’.
Ans: Jatin Sarkar was a bank officer. After retirement he came back to his forefather’s house. He requested the tenant to vacate the house. But the tenant did not vacate the house. Tenant challenged that if Jatin Sarkar wanted to have his house vacated, he should move to court for justice. He was compelled to live in a rented house. The owner lodged litigation against the tenant. After fighting the case for five years, the owner won the case. The decision was made in his favour by the Trial Court. But the tenant appealed in the High Court against the lower court decision. It again took five years for justice. In the meantime Jatin Sarkar kept on living in the rented house because unless there was judgment, he had no other option. In such a situation we can definitely say, ‘Justice delayed is justice denied’.
8. Make sentences with each of the glossary words given on the next page.
Ans:
i) Acquit: Two members of the group were acquitted for lack of evidence.
ii) To appeal: When the girl was lost, her parents appealed to the public for information.
iii) Compensation: Her salary is still far lower that the high compensation of her predecessors, which had led to criticism by state auditors and helped fuel restructuring of the agency by the Legislature.
iv) Eviction: The landlord was forced to file an eviction lawsuit in court after the tenants were three months behind in rent and refused to pay.
v) Violation: India had said its soldiers were able to stop a push by Chinese troops to claim more ground in violation of existing agreements, while Beijing denied its troops had strayed into Indian Territory.
9. The following is a poster made by the Right to Food campaign.
Read this poster and list the duties of the government to uphold the Right to Food.
i) How does the phrase “Hungry stomachs, overflowing godowns! We will not accept it!” used in the poster relate to the photo essay on the right to food on page 61?

Ans: India is a democratic country and it believes in the welfare of the people. Human Rights as well as the Constitution of India uphold the right to live. Without food nobody can live for long period of time. It is the fundamental duty of the government to provide at least minimum food items to the poor people either totally free or at a very nominal cost. The mid – day meal program is a good example that is performed to uphold the Right to Food to the Children studying at primary or even middle level.

