ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS:
1) Write the six elements of Δ PQR.
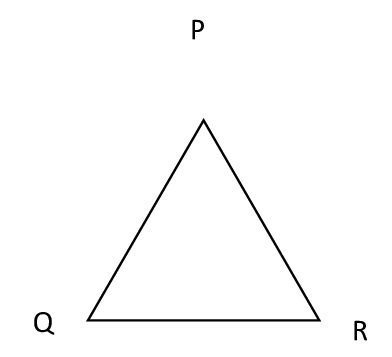
Ans:
The six elements of the triangle are:
3 sides are PQ ,PR and QR and 3 angles are ∠P ∠Q and ∠R.
2) Classify the following triangles according to its
a) Sides b) Angles
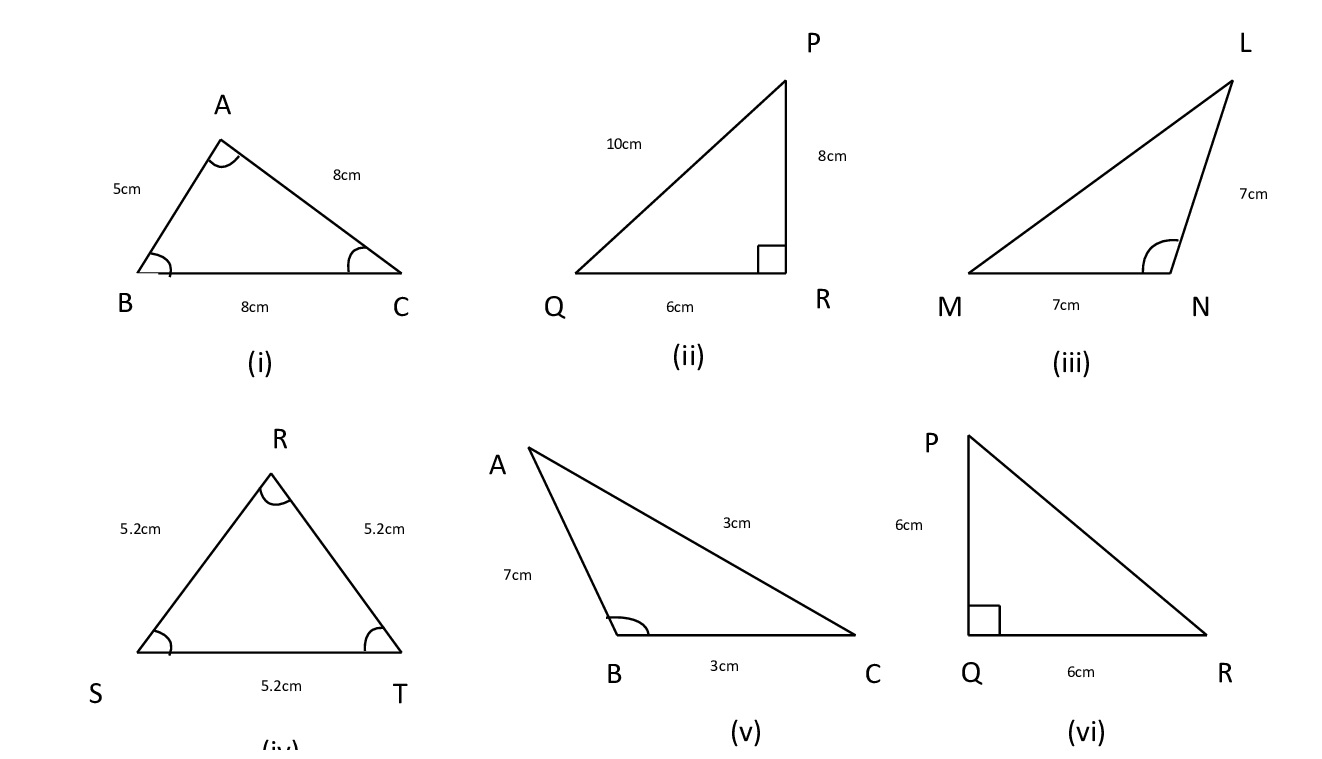
Ans:
Angles and Sides
i) In ΔABC , all angles are acute
∴ It is an acute – angled triangle
ii) In ΔPQR , ∠R is a right angle
∴ It is a right – angled triangle.
iii) In ΔMNL , ∠N is an obtuse angle ∴It is an obtuse – angled triangle
iv) In ΔRST all angles are acute
∴ It is an acute – angled triangle
v) In ΔABC ∠B is an obtuse angled triangle ∴ It is an obtuse – angled triangle
vi) In PQR , ∠Q is a right angle ∴ It is an right – angled triangle.
i) In ΔABC , AC= BC
∴ It is an isosceles triangle.
ii) In ΔPQR , QR ≠ RP ≠ PQ
∴ It is a scalene triangle.
iii) In ΔLMN , MN = LN
∴ It is an isosceles triangle.
iv) In ΔRST , RS = ST = RT
∴ It is an equilateral triangle.
v) In ΔABC , AB = BC
∴ It is an isosceles triangle.
vi) In ΔPQR , PQ = QR
∴ It is an isosceles triangle.
b) Angles
i) In ΔABC , all angles are acute
∴ It is an acute angled triangle.
ii) In ΔPQR , ∠R is a right angle
∴ It is a right – angled triangle.
iii) In ΔMNL , ∠N is an obtuse angle
∴ It is an obtuse – angled triangle.
iv) In ΔRST , all angles are acute
∴ It is an acute – angled triangle.
v) In ΔABC , ∠B is an obtuse angle
∴ It is an obtuse – angled triangle
vi) In ΔPQR , ∠Q is a right angle
∴ It is a right – angled triangle.
3) In ΔLMN , write the following: 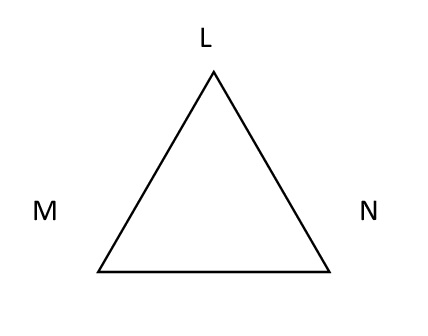
a) A side opposite to ∠MNL.
b) Angle opposite to side ML.
c) Vertex opposite to side NL.
d) Side opposite to vertex L.
Ans:
a) LM
b) ∠LNM or ∠MNL
c) M
d) MN
4) An exterior angle of a triangle is of measure 70ᵒ and one of its interior opposite angles is a measure of 25ᵒ.
Find the measure of the other interior opposite angle.
Ans: Sum of interior opposite angles = exterior angle
Let the unknown interior angle be x
Then, x + 25ᵒ = 70ᵒ
x = 70ᵒ − 25ᵒ ⟹ x = 45ᵒ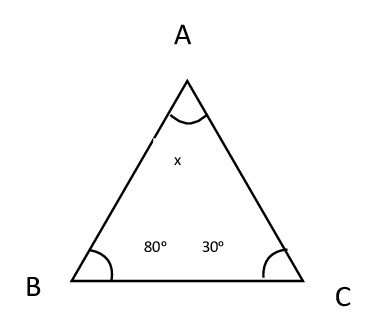
5) Two angles of a triangle are 30ᵒ and 80ᵒ. Find the third angle.
Ans:By angle sum property of a triangle
x + 30ᵒ + 80ᵒ = 180ᵒ
x + 110ᵒ = 180ᵒ
x = 180ᵒ − 110ᵒ ⟹ x = 70ᵒ
6) The three angles of a triangle are in the ratio of 1 : 2 : 1.
Find all the angles of the triangle.
Ans: Let the common variable be x.
Let the first angle be 1 x.
Let “ second “ be 2 x.
Let “ third “ be 1 x.
By the angle sum property of triangle,
1 x + 2 x + 1 x = 180ᵒ
4 x = 180ᵒ
x = 180ᵒ/4 ⟹ x = 45ᵒ
∴ The first angle = 1 x = 1 x 45ᵒ = 45ᵒ
The second angle = 2 x = 2 x 45ᵒ = 90ᵒ
The third angle = 1 x = 1 x 45ᵒ = 45ᵒ
7) Find the angle x in each figure:
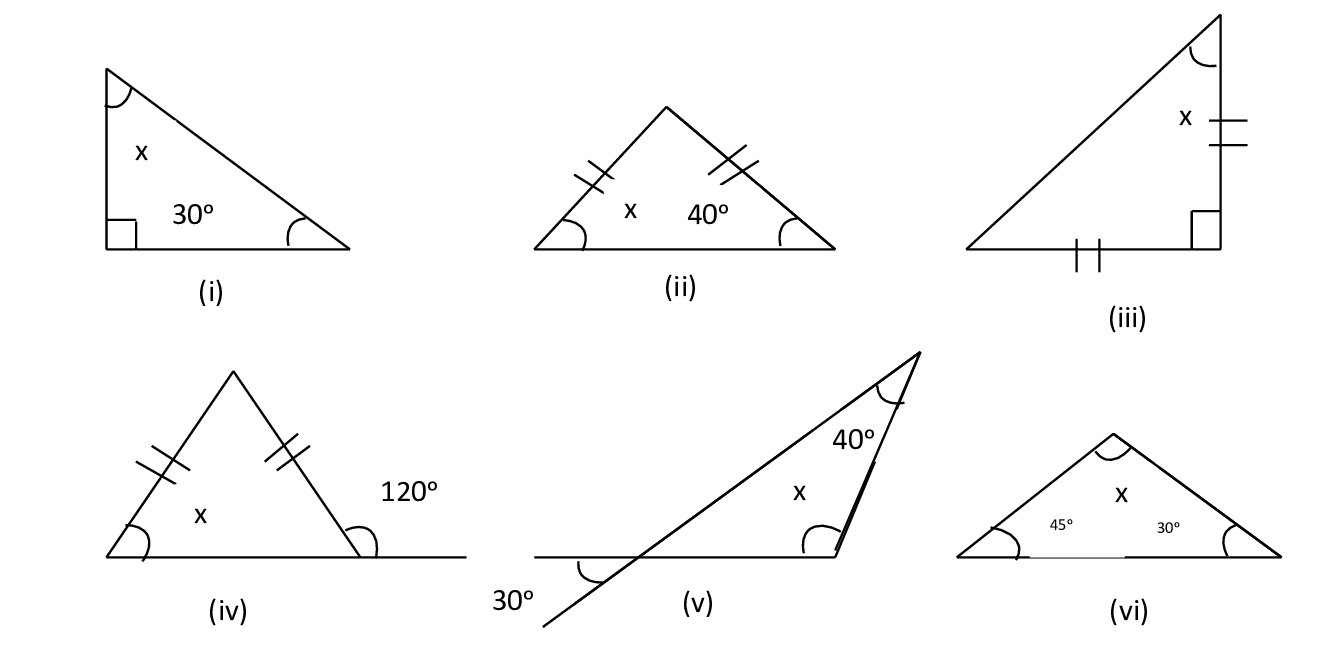
Ans:
i) By angle sum property
x + 90ᵒ + 30ᵒ = 180ᵒ
x + 120ᵒ = 180ᵒ
x = 180ᵒ – 120ᵒ
x = 60ᵒ
Since the triangle has 2 equal sides, let both angles of the equal sides be x.
∴ x + x + 40ᵒ = 180ᵒ —- (angle sum property)
ii) 2x + 40ᵒ = 180ᵒ
2x = 180ᵒ – 40ᵒ
2x = 140ᵒ
x = 140ᵒ/2 ⟹ x = 70ᵒ
Since the triangle has 2 equal sides, let both angles of the equal sides be x.
∴ x + x + 90ᵒ = 180ᵒ — (angle sum property)
iii) 2x + 90ᵒ = 180ᵒ
2x = 180ᵒ – 90ᵒ
2x = 90ᵒ ⟹ x = 90ᵒ/2 ⟹ x = 45ᵒ
Since the triangle has 2 equal sides, let both angles of the equal sides be x.
x + x = 120ᵒ —- (exterior angle property)
2x = 120ᵒ ⟹ x = 120ᵒ/2 ⟹ x = 60ᵒ
iv) Let the third angle of the triangle be y
y = 30ᵒ —- (vertically opposite angles)
By angle sum property
x + y + 40ᵒ = 180ᵒ
x + 30ᵒ + 40ᵒ = 180ᵒ
x + 70ᵒ = 180ᵒ
x = 180ᵒ – 70ᵒ ⟹ x = 110ᵒ
By angle sum property of triangle
x + 30ᵒ + 45ᵒ = 180ᵒ
x + 75ᵒ = 180ᵒ
x = 180ᵒ – 75ᵒ ⟹ x = 105ᵒ
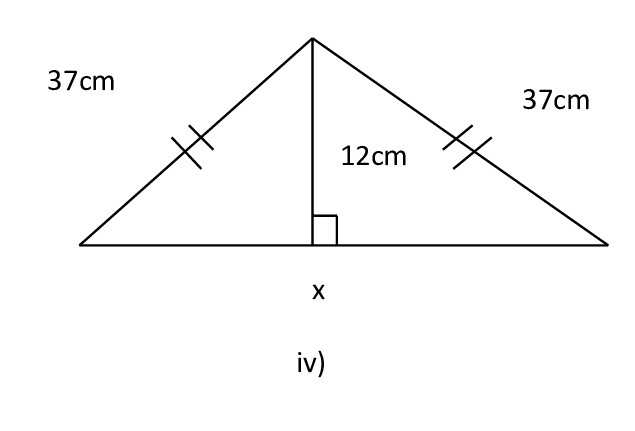
8) Find the length of x in the following figures:
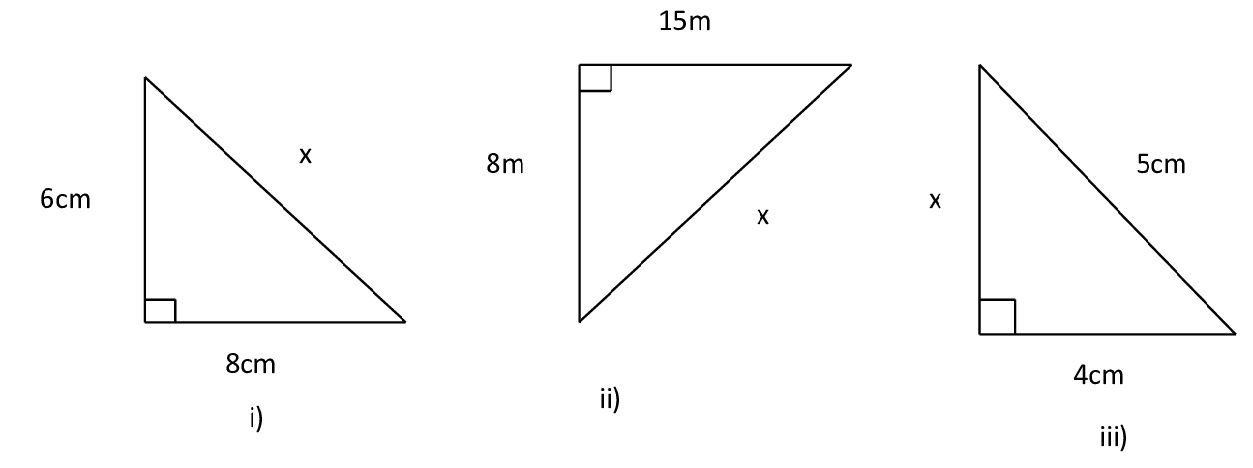
 Ans:
Ans:
By Pythagoras theorem,
x 2 = 62 + 82
x 2 = 36 + 64
x 2 = 100
x = √100 ⟹ x = 10
∴ x = 10 cm
By Pythagoras theorem,
x 2 = 152 + 82
x 2 = 225 + 64
x 2 = 289 ⟹ x = √289 ⟹ x = 17 cm
By Pythagoras theorem,
52 = x 2 + 42
x 2 = 52 – 42
x 2 = 25 – 16
x 2 = 9 ⟹ x = √9 ⟹ x = 3 cm
Let the triangle be ABC. Let BD be perpendicular line on AC.
In Δ BDC
BC 2 = BD 2 + DC 2
372 = 122 + DC 2
DC 2 = 372 – 122
DC 2 = 1369 – 144
DC 2= 1225
DC = √1225
DC = 35
The perpendicular BD bisects side AC hence AD = DC
∴ AD + DC = x
35 + 35 = x
∴ x = 70 cm
9) In the given figure, name the median and the altitude, here ε is the midpoint of BC.
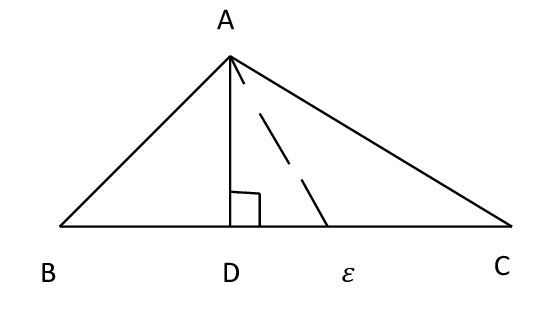
Ans:
i) Median = Aε ii) Altitude = AD
10) The sides of a triangle are in the ratio 3 : 4 : 5. State whether the triangle is right – angled or not.
Ans: Let the sides of the given triangle be 3 x, 4 x and 5 x.
For a triangle to be right – angled
Square of the larger side = sum of squares of other two sides
(5 x)2 = (3 x)2 + (4 x)2
25x 2 = 9 x 2+ 16x 2
25x 2 = 25x 2
Hence, the given triangle is a right – angled triangle.

