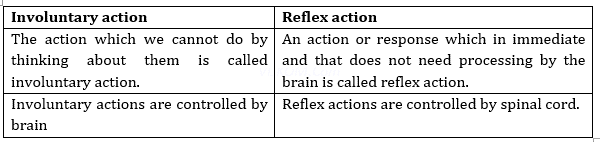
1. How involuntary actions and reflex actions are different form each other.
Ans.
2. Name the centre of the brain that controls
(i) Swallowing (ii) hearing
Ans.(i) Medulla oblongata in hind brain —- Swallowing
(ii) Cerebrum in fore brain —- Hearing
3. Which signal will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury.
Ans.(i) It distrupts all the involuntary actions.
(ii) Reflex actions will be disrupted because reflexes are located in the spinal cord.
Therefore, the quick response required to safeguard the body will not take place.
4. How does a touch me not plant respond on touching. What is this movement called?
Ans. Touch me not plant folds its leaflets on touching. This type of movement is called growth independent movement.
5. What are phytohormones? Name them.
Ans. Phytohormones are special chemical compounds released by different parts of plant. They help to co ordinate growth, development and responses to the environment. They are synthesized at site away from where they act and simple diffuse to the area of action. These are – Auxin, Gibberlins, Cytokinin, Abscisic acid, Ethylene.
6. What is the role of the brain in reflex action.
Ans. A reflex action is one which we perform automatically. The sensory and motor nerves meet at a point in the spinal cord on their way to the brain. Thus the information through sensory nerves goes to the brain, where thinking process occurs. But if the reflex action is instant where thinking in not involved then the brain has no role.
7. What are two types of plant responses.
Ans. Plants responses are mainly of two types –— Growth dependent and growth in dependent response.
Growth in dependent Responses are because of change in the amount of water. Growth dependent responses are due to cell divisions.
8. Give two examples of function in plants that are regulated by light
Ans. 1) Phototropism 2) Photosynthesis
9. What is coordination. Give an example.
Ans. The working together of the various systems in a body to adjust the vital activities of life is called co ordination. E.g – the nervous system receives information form the surroundings, then processes and interprets it and finally responds accordingly. The endocrine system helps in control and co ordination.
10. Which types of glands in human body secrete hormones. State any one location for them.
Ans. There are three types of glands which secrete hormone in the human body-
a) Exocrine gland – these are duct glands which do not secrete their secretion into the blood. F – Eg: Salivary gland. it secretes salivary amylase which digest starch.
b) Endocrine gland – These are ductless gland, and they pour their secretion in blood. Eg:– Pituitary gland. It is master gland, controls most of the activities.
c) Heterocrine gland – which act as both endocrine and exocrine type of glands. Eg: Pancreas – endocrine part produces hormone insulin and glycogen and exocrine part produce digestive enzymes.
11. What is the result of hypothyroidism in children called.
Ans. Hypothyroidism in children called exophthalmic goiter. It causes bulging of eyes, increases blood pressure and heart beat.
12. How do hormones affect plants.
Ans. Hormones like Auxins, Cytokinin promotes female flowers. whereas Gibberellins promote male flowers. Ethylene promote flowering in some plants like pineapple Phytohormones and duration of light also induce flowering in long day plants and short day plants.
13. Name the fluid filled between the meninges of the brain. What are its functions.
Ans. Cerebro spinal fluid. It protects the brain form mechanical shocks.

