1. Define reproduction. Why is it important.
Ans. It is a process by which organisms are able to produce new organisms of their own kind. It is important to maintain the continuity of life.
2. What is callus.
Ans. In artificial vegetative propagation, an isolated plant part called explant is cultured in a glass container under aseptic conditions with proper nutrient medium. The explant develops into an undifferentiated mass of cells called callus.
3. What happens if the mature ovum is not fertilized in a female. Name the process
Ans. If a mature egg is not fertilized it gets released into fallopian tubes. This process is known as menstruation.
4. Give the full form of (i) IUCD (ii) STD.
Ans.
(i) Intra Uterine Contraceptive Device.
(ii) Sexually Transmitted Diseases.
5. What do you understand by self-pollination & cross-pollination. Give examples of each.
Ans. Self-pollination – It is the transfers of pollen grains from an anther to the stigma of the same plant. If it is in the same flower, it is called autogamy and if it is between flowers of the same plant, then it is called geitonogamy.
Cross-pollination – It is the transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma of different plants of the same species.
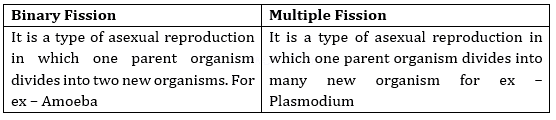
6. What is the difference between binary fission and multiple fission?
Ans.
7. What are the basic features of asexual reproduction?
Ans. Basic feature for asexual reproduction are:
(1) Only one organism is involved.
(2) Cell divisions are either amitotic or mitotic.
(3) New organisms are genetically identical to parents.
(4) Formation of gametes and their fertilization does not occur.
8. What is a clone. Why do offspring’s formed by asexual reproduction exhibit remarkable similarity?
Ans. Cells derived from a common ancestor are known as a clone. Offspring obtained from asexual reproduction has only one parent, there are no chances of variation in their chromosomes. Hence, they are exactly similar with their parents.
9. List two important functions of gonads.
Ans. a) It produces gametes in male and female
b) It produces sex hormones
10. What is the function of Cowper’s gland and prostate gland?
Ans. Cowper’s glands – It secretes a white, viscous and alkaline secretion which acts as a lubricant.
Prostate gland – The secretion of this gland keeps the sperm active and mobile.
11. List various reproductive parts of the flower
Ans. Reproductive organs of flower are –
a) Androecium (male reproductive part) – It has two parts filament and anther. Another has four pollen sacs which contain pollen grains. Pollen grains produce two male gametes.
b) Gynoecium (Female reproductive part) – It has three parts – ovary, style and stigma.
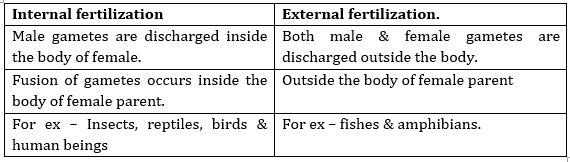
12. What is the difference between internal & external fertilization.
Ans.
13. Name the type of reproduction involved in the following –
(i) A slice of bread has greenish-yellow patches.
(ii) Potato in the storeroom starts sprouting
Ans. i) Spore formation ii) Vegetative propagation
14. Give two reasons for the appearance of variations among the offsprings formed by sexual reproduction.
Ans. An offspring produced by sexual reproduction has variations because –
a) It involves two parents, so the offspring has some characteristics of male and some of the female.
b) Copying of DNA is not exactly the same as the parent.
15. Name the organism causes syphilis. Mention two symptoms.
Ans. Syphilis is caused by bacteria. Symptoms are –
a) Causes sores and lesions in the genital tract.
b) Burning sensation at urination.
16. How does human foetus derive nutrition?
Ans. A special disc-like structure is formed between the embryo and the uterus wall called the placenta. It is a connection between the mother and the foetus. This disc remains embedded in the uterine wall. It contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue. On the mother’s side are blood spaces, which surround the villi. This provides a large surface area for the transfer of nutrients mother to foetus.
17. Why are testes and ovaries considered as primary sex organs?
Ans. Testis and ovaries are called primary sex hormones because they produce gametes and sex hormones. They are responsible for the control and onset of the whole reproduction system.
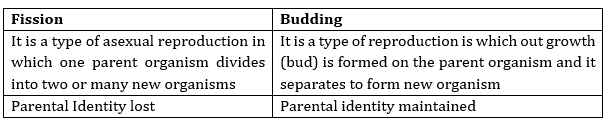
18. What is the difference between fission and budding?
Ans.
19. Mention function of testis in humans.
Ans. Function of testes –
a) Spermatogenesis: – Testes produce male gametes sperm.
b) Secretion of hormone: – Testes secrete hormone testosterone – the male sex hormone which helps in regulation of sperms and also maintains structure and function of secondary sex characters like facial, and pubic hair, voice moustache, etc.
20. Why does menstruation occur.
Ans. When an ovum does not get fertilized, due to non availability of sperm in the female body, then longer needed and hence it breaks. So, the thick and soft inner lining of uterus along with the blood vessels and the dead ovum comes out of the vagina in the form of blood, called menstruation.

