1) Give an example of a metal which
(i) is a liquid at room temperature. (ii) Can be easily cut with a knife.
(iii) is the best conductor of heat. (iv) is a poor conductor of heat.
Ans:
(i) metal that exists in liquid state at room temperature → Mercury
(ii) metal that can be easily cut with a knife → Sodium, Potassium
(iii) metal that is the best conductor of heat → Silver, Gold
(iv) metals that are poor conductors of heat → Mercury and Lead
2) Explain the meanings of malleable and ductile.
Ans: Substances that can be converted into thin sheets by beating are called malleable. Most of the metals are malleable. Gold and Silver are most malleable metals. Substances that can be drawn into thin wires are called ductile. Most of the metals are ductile. Gold and Silver are the most ductile metals.
3) Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Ans: Metals such as potassium and sodium react so vigorously that they catch fire if kept in the open. Hence, to protect them and to prevent accidental fires, they are kept immersed in kerosene oil.
4) Write equations for the reactions of
(i) Iron with steam (ii) Calcium and Potassium with water
Ans:
(i) Iron reacts with steam to form the metal oxide and hydrogen.
3 Fe(s) + 4 H2O (g) → Fe3o4 (s) + 4 H2 (g)
(ii) the reaction of Calcium with water is exothermic but the heat evolved is not sufficient for the Hydrogen to catch fire.
Ca (s) + 2 H2O (l) → Ca (OH)2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Calcium starts floating because the bubbles of Hydrogen gas formed stick to the surface of the metal.
Potassium react violently with cold water and its reaction is so violent and exothermic that the evolved Hydrogen immediately Catches fire.
2 K (s) + 2 H2O (l) → 2 KOH (aq) + H2 (g) + heat energy
5) Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows.
| Metal | Iron sulphate | Copper sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | ||
| B | Displacement | No reaction | ||
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the table above to answer the following about metals A, B, C and D.
(i) Which is the most reactive metal?
(ii) What would you observe if b is added to a solution of copper (ii) sulphate?
(iii) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Ans:
(i) B is the most reactive metal since B can displace iron from its sulphate,
(ii) As B is more reactive than iron, so it will displace copper from its copper sulphate solution.
(iii) B is most reactive and D is the least reactive metal as unable to displace any of the solutions. Copper is more reactive than silver and metal A can displace copper, so A is more reactive than C.
Hence, the order of decreasing reactivity is B > A > C > D.
6) Which gas is produced when dilute Hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal? Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4.
Ans: When reactive metals react with dilute Hydrochloric acids, gives a salt and hydrogen gas
Metal + dilute acid → salt + hydrogen.
Reaction between iron and H2SO4: ⇒ Fe + H2SO4 → FeSO4 + H2
7) What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Ans: Zinc is more reactive than iron. When Zn is added to iron (II) sulphate, zinc displaces iron from its solutions and zinc sulphate is formed.
Zn (s) + FeSO4 (aq) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
8)
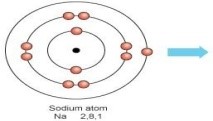
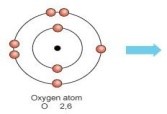
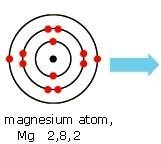
(i) Write the electron-dot structures for Sodium, Oxygen and Magnesium.
(ii) Show the formation of Na2O and MgO by the transfer of electrons
(iii) What are the ions present in these compounds?
Ans:
Magnesium —- dot structure Sodium —- dot structure Oxygen — dot structure
![]()

![]() fig
fig
(ii). Formation of Na2O by transfer of electron:
fig: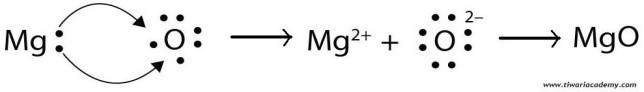
(iii). Ions present in these compounds are Mg++, O– – and Na+.
fig:
Ans: Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points. because ionic compounds are formed by the attraction force of two opposite ions and a considerable amount of energy is required to break this strong inter-ionic band attraction. 2: Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
9) Define the following terms.
(i) mineral (ii) ore (iii) gangue.
Ans: (i) The elements or compounds, which occur naturally in the earth’s crust, are known as minerals.
(ii). If minerals contain a very high percentage of a particular metal and the metal can be profitably extracted from it. Then these minerals are called ores.
(iii). Ores mined from the earth are usually contaminated with large amounts of impurities such as soil, sand, etc., These impurities are called gangue.
10) Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
Ans: The metals which are the least reactive, they are often found in a free state.
e.g: gold, silver, platinum and copper are found in the free state.
11) What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
Ans: Metals low in the activity series are very unreactive. The oxides of these metals can be reduced to metals by heating alone.
2 HgO (s) —→ 2 Hg (l) + O (g)
The metals in the middle of the activity series such as iron, zinc, lead, copper, etc., are moderately reactive. These metal oxides are reduced to the corresponding metals by using suitable reducing Agents
ZnO (s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO (g)
The metals high up in the reactivity series are very reactive. They are separated from their oxides by the electrolysis process.
12) Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals.
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper |
| Zinc oxide | No reaction | Yes | No |
| Magnesium oxide | No | No | No |
| Copper oxide | Yes | Yes | No |
Ans: Magnesium is the most reactive among these three metals and zinc is more reactive than copper. So, magnesium will displace zinc oxide and copper oxide whereas zinc will displace copper oxide only.
13) Which metals do not corrode easily?
Ans: The metals which are the least reactive, do not corrode easily.
e.g: gold, silver, platinum and copper.
14) What are alloys?
Ans: An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal.
e.g: Stainless steel is an alloy of Nickel and Chromium.
Amalgam is an alloy of mercury.
Brass is an alloy of copper and zinc.
Bronze is an alloy of copper and tin.
Solder is an alloy of lead and tin.

